Data should be recognized as a valued and strategic asset of the University
-
Data is a critical asset of the University as it enables and drives day-to-day operational and decision-making processes
-
Data is also a liability of the University in the sense that mishandling or misuse of data can lead to catastrophic legal or operational consequences for the University and individual members or stakeholders
-
Handling and use of data must benefit the University and individual members or stakeholders

Data should have clearly defined accountability
- Data owners are individuals who are accountable for the data domains they own, with help from:
- Data stewards who understand the specifics about the data in concern throughout the data life cycle
- Data custodians who advise and implement the necessary technical development and management functions over the data in concern
- Data stewards who understand the specifics about the data in concern throughout the data life cycle
- Data analysts and data users are individuals who make productive and legitimate use of the data in concern, conforming to the data access requirements as stipulated by data owners

Data should be managed to follow internal and external rules
-
Handling and use of data must conform with respective laws and regulations
-
Justifiable-Business-Needs – Creation, update, retention, and access should be justified based on actual operational or analytical needs, for supporting University business rather than any other interests
-
Shared-Responsibilities – Maintaining an effective and efficient data governance
is in the interest of, and requires the contribution from, every member of the University, in the sense of a “shared-responsibilities” model
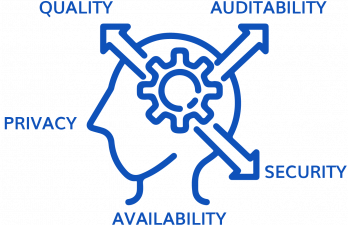
Data management issues should be defined and addressed throughout the entire data lifecycle
-
Data management issues pertaining to the quality, privacy, security, availability, and auditability should be considered and planned throughout the entire data lifecycle
-
Single-Source-of-Truth – Duplication of data should be avoided as much as possible to minimize possible confusions that can undermine credibility of data